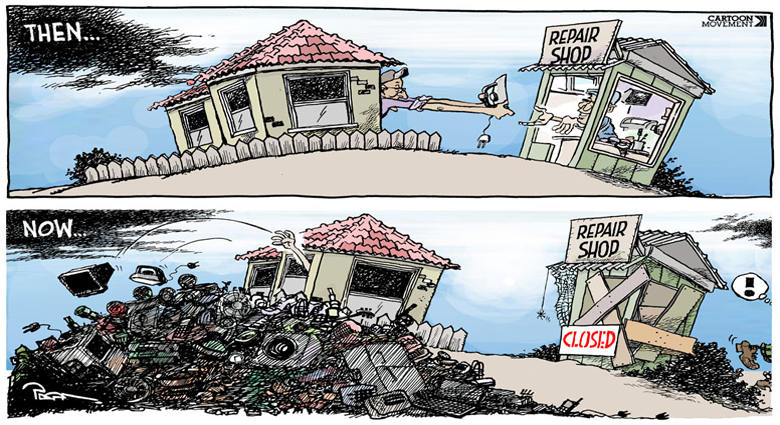
The abundance of resources and raw materials in the industrial age led to the development of a throwaway society, and as resources run out, the many facets of sustainability become a more important focus for designers. The result of the throwaway society is large amounts of materials found in landfill, which can be considered as a new source to mine resources from.
Strategies to Mitigate Waste
Re-use
Term: This is reusing a product in the same context or in a different context.
- Reusing is utilising an object more than one time.
- This takes into account of conventional reuse where the object is used again for similar purpose, and new-life reuse where it is used for an innovative purpose.
- An example of reusing is using disposable plastic or glass bottles to drink water from over again.
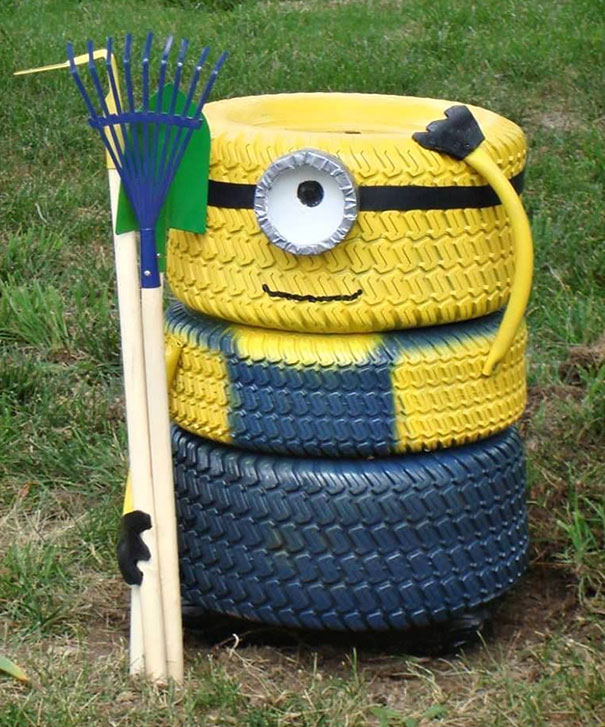
- Reusing car tyres
|
|
Recycle
Term: Recycling refers to using the materials from obsolete products to create other products.
- Recycling consists of processing used materials into novel products in order to avert squandering potentially functional materials.
- It decreases the consumption of unsullied raw resources, trims down energy usage, lowering air and water pollution by dropping the need for “usual” waste discarding, and lastly lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- An example of recycling is recycled paper.
Repair
Term: Is the reconstruction or renewal of any part of an existing structure or device.
Recondition
Term: Reconditioning is rebuilding a product so that it is in an “as new” condition, by repairing it, cleaning it, or replacing parts.
- Contexts include car engines, tyres or refurbished electronics.
Re-engineer
Term: A re-engineered product has been significantly redesigned, with improved engineering, from its original form.
- In may: use raw materials that were meant another product or manufacturing process, use environmentally friendly materials, recycle some of the original components, improve performance.
- The Dyson Ball Vacuum cleaner has been re-engineered. The vacuum still functions in collecting dust but the method of doing it is different. They redesigned the suction system.
Pollution & Waste
From Wikipedia “Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change.[1] Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light. Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be either foreign substances/energies or naturally occurring contaminants.

From Wikipedia, Wastes are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance which is discarded after primary use, or it is worthless, defective and of no use.
Something to ponder? – This is subjective as one persons idea of waste may whereas another person may find it useful!
- Smokey Mountain in the Philippines
- Zabbaleen of Mokkattam in Cairo
Methodologies for Waste Reduction and Designing out Waste
Dematerialization
Term: The reduction of total material and energy throughput of any product and service.

- Dematerialization improves product efficiency by saving, reusing or recycling materials, components and products.
- It impacts on every stage of the product life cycle: in material extraction; eco-design; cleaner production; environmentally conscious consumption patterns; recycling of waste.
- It may mean smaller, lighter products and packaging; the replacement of physical products by virtual products (email instead of paper, web pages instead of brochures); home working, and so on.
- Reduction of total material and energy throughput of a product or service, and the limitation of its environmental impact through: reduction of raw materials at the production stage; energy and material inputs at the user stage; waste at the disposal stage
- There are potential results of successful dematerialization ..
Product Recovery Strategies at End of Life/Disposal
Term: The processes of separating the component parts of a product to recover the parts and materials.
- Use and recovery of standard parts at the end of product life.
- Recovery of raw materials.
- Take back legislation.
- Trade in.
- Recycling bins/locations.
- Employ a circular economy.
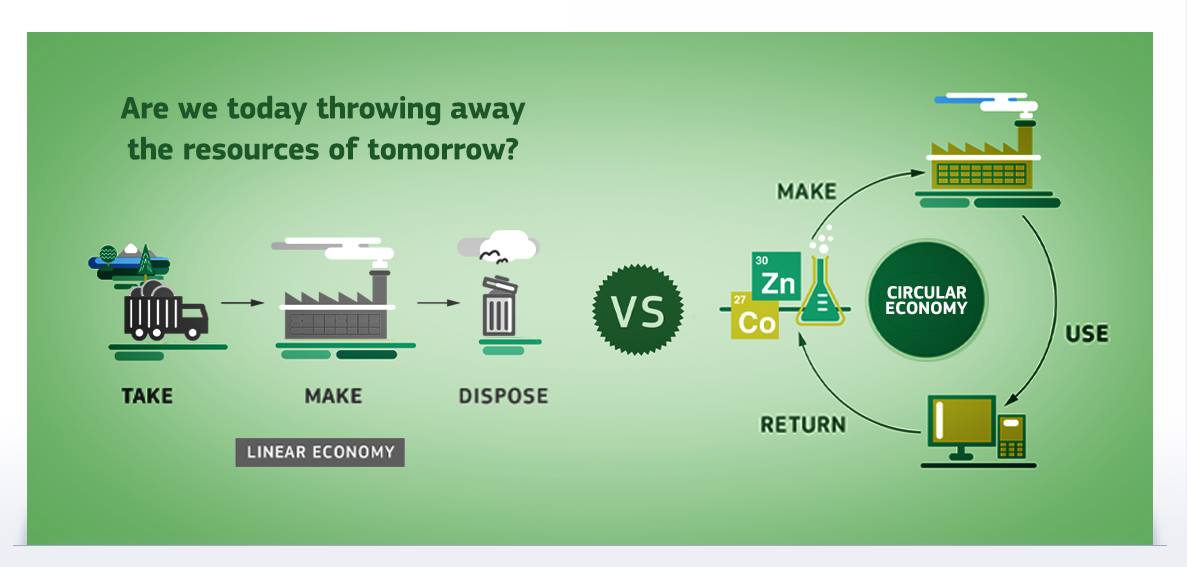
Circular Economy
Term: An economy model in which resources remain in use for as long as possible, from which maximum value is extracted while in use, and the products and materials are recovered and regenerated at the end of the product life cycle.
- In an economic model that is a closed loop system where the materials/resources are in constant use. At the end of the product life cycle the material waste (or obsolete product material) is recycled/recovered.
- The material waste is a resource in the system and is regenerated at he end of the product life cycle.
- A circular economy requires designers to consider the subsequent use of materials, components and the embedded/embodied energy in a product.
- This can only be achieved by innovative design and consideration of further cycles of development.
- Designers must ask themselves the question, “How can this product be made to be made again?”
- There are three central strands to this concept:
- cradle-to-cradle (Topic 2.6) design thinking which looks at the whole design and manufacturing process.
- design for disassembly (Topic 4.5) which allows for recovery of materials and components.
- design inspired by nature that favours diversity and in which there is no waste (biomimicry).
- Innovative design techniques might include:
- the use of smart (shape) memory screws,
- dissolvable circuit boards and adhesives (glue),
- the use of clips rather than adhesives or screws,
- biological materials (such as bioplastics) that can be safely returned to the biosphere with no toxic dyes or other materials.
- Equally important are the systems in which the product moves: How will the materials or components be recovered and made use of again.
- The designer and manufacturer need to consider this when developing products.
- One way forward is to develop different business models where users buy performance through leasing rather than purchasing. This offers interesting job opportunities in creating reverse supply chains as well as engaging design challenges and opportunities.
- Splosh – A company has set where a customer purchases a one-off starter kit and then fill the bottle with a sachet of cleaning liquid add warm water and they already to go.
- The adding water reduces packing (reduction of materials) and weight (important for transportation – reduction is fuel)
- Saves on materials, energy and waste.
- If the bottle is reused 20 times it means 95% less packaging waste

-
- The above models show the traditional linear, where material is extracted, manufactured and diseased in landfill. The circular model – one of them the bio-waste is returned to enrich the earth. The left model the technical waste is recycled and rescued in the continued production.
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation of Circular economy includes overview, diagrams and case studies.
Final Word: Designing out waste and designing for closed-loop recycling will be more important as resources become scarcer and waste becomes more expensive. Therefore, developing products for product recovery and dematerialization will become an essential element of innovation.
International Mindedness
The export of highly toxic waste from one country to another is an issue for all stakeholders.
Theory of Knowledge
The circular economy can be seen as an example of a paradigm shift in design. Does knowledge develop through paradigm shifts in all areas of knowledge?
Something Extra …






/article-new/2021/02/refurbished-iphone-11.jpg)